8 Primitive Types
1. Short answer
Java has 8 primitive data types:
- byte -> 8-bit integer, range: -128 to 127
- short -> 16-bit integer, range: -32,768 to 32,767
- int -> 32-bit integer, range: -231 to 231 -1
- long -> 64-bit integer, range: -263 to 263 -1
- float -> 32-bit floating-point number
- double -> 64-bit floating-point number
- char -> 16-bit Unicode character
- boolean -> Represents true or false
These types are used to store simple values and are more memory-efficient than objects.
2. Long answer
In Java, most work is done with primitives. These primitive data types are the foundation of all other types.
- They are used to store simple values such as numbers and characters.
- They are stored directly in memory and are accessed faster than non-primitive data types.
There are eight primitive data types in Java: byte, short, int, long, float, double, char and boolean.
The size and range of values that can be stored in a primitive data type depending on the type itself. For example, a boolean can only hold the values true or false, while a long can hold values from -263 to 263-1.
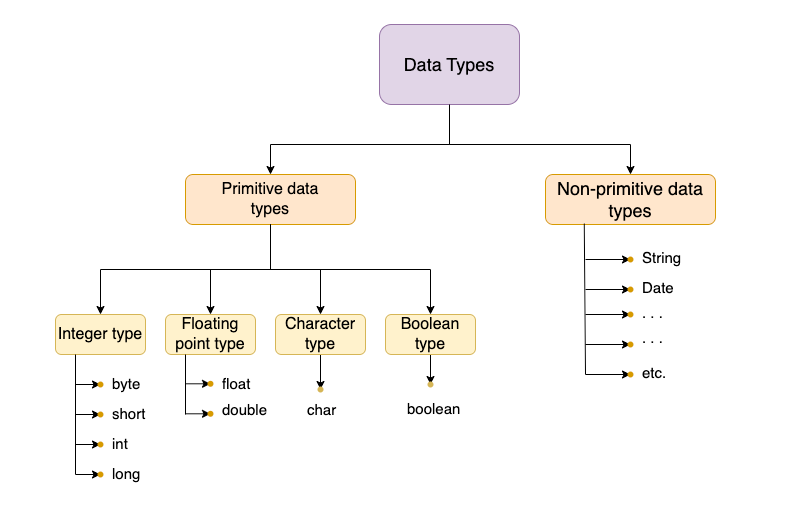
Hence, the 8 primitive data types in Java are categorized into 4 types.
- Integer types -
byte,short,int, andlong. - Floating point types -
floatanddouble. - Character type -
char. - Boolean type -
boolean.
Illustration
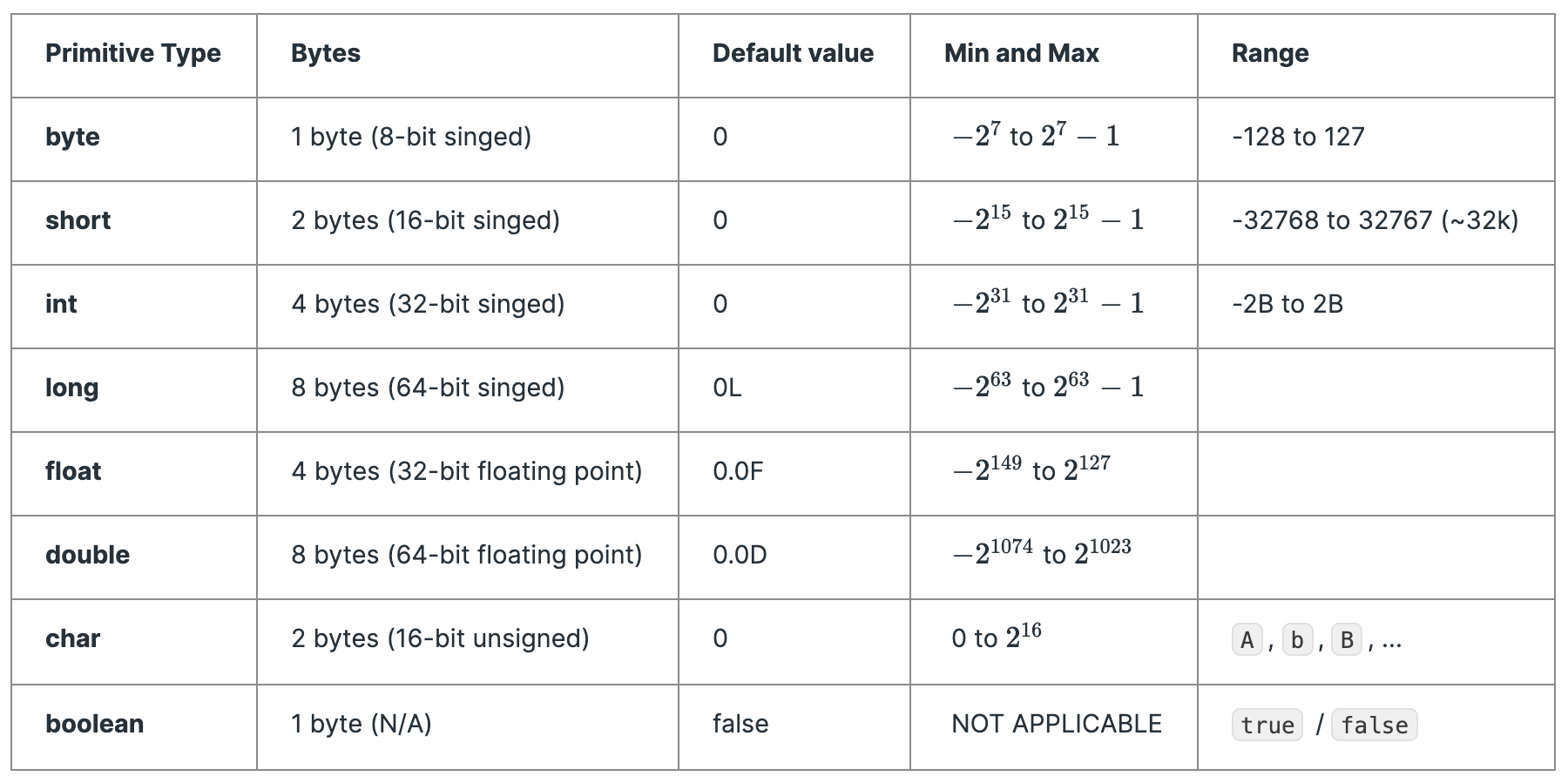
Tabular chart
Let us see the bytes size, default value, min and max and ranges of all the primitive data types.
1. byte
A byte is an 8-bit signed integer occupies 1 byte, default value is 0, and it can store a minimum value of -2^7 or -128 and a maximum value of (2^7 - 1) or 127.
The maximum and minimum values of byte can be found at:
byte high = Byte.MAX_VALUE; // high == 127
byte low = Byte.MIN_VALUE; // low == -1282. short
A short is a 16-bit signed integer.
- Occupies
2bytes. - The default value is
0. - It can store a min value of
-2^15or-32768and a maximum value of(2^15 - 1)or32767.
short A = -48;
short B = 987;
short C = 17;
short add = (short) (B + C);
short subtract = (short) (B - C);
System.out.println(add); // 1004
System.out.println(subtract); // 970The maximum and minimum values of short can be found at:
short high = Short.MAX_VALUE; // high == 32767
short low = Short.MIN_VALUE; // low = -327683. int
This is one of Java's most used data types, storing 4 bytes of data. According to Java API, the Integer class wraps a value of the primitive type int in an object.
An int is a 32-bit signed integer.
- Occupies
4bytes. - The default value is
0. - It can store a min value of
-2^31or-2Band a maximum value of(2^31 - 1)or2B.
int A = -48;
int B = 987;
int C = 17;
int add = B + C;
int subtract = B - C;
System.out.println(add); // 1004
System.out.println(subtract); // 970The maximum and minimum values of short can be found at:
int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // -2147483648
int min = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // 21474836474. long
By default, long is a signed integer (In Java 8, it can be either signed/unsigned).
Signed: It can store a minimum of 263 and a maximum of 263 - 1).
Unsigned: It can store a minimum value of 0 and a maximum value of 264 - 1).
- Occupies
8bytes. - The default value is
0L.
If you assign long A = 100, Java assumes it as a int type. Appending L makes it a long.
long A = -42;
long B = 284;
long C = 73;
long bigNumber = 549755813888L;
long addedLongs = B + C; // 284 + 73 = 357
long subtractedLongs = B - C; // 284 - 73 = 211
System.out.println(addedLongs); // 357
System.out.println(subtractedLongs); // 211The maximum and minimum values of long can be found at:
// Max and Min
long high = Long.MAX_VALUE; // high == 9223372036854775807L
long low = Long.MIN_VALUE; // low == -9223372036854775808LNote: LetterLappended at the end of thelongliteral is case insensitive, however it is good practice to use capital as it is easier to distinct from digit one.
2L == 2l // true5. float
A float is a single-precision 32-bit floating point number.
- Occupies
4bytes. - The default value is `0.0F`.
- It can store a min value of
-2^149and a maximum value of2^127.
By default, decimals are interpreted as doubles. To create a float, append an f to the decimal literal.
A float is precise to roughly an error of 1 in 10 million.
Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY
Float.NEGATIVE_INFINITY
Float.NaNNaN stands for the results of an operation that cannot be determined. Such as dividing two infinite values.
float f1 = 0f;
float f2 = -0f;
System.out.println(f1 == f2); // true
System.out.println(1f / f1); // Infinity
System.out.println(1f / f2); // -Infinity
System.out.println(Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY / Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY); // NaN0f and -0f are different but == yields true.
// addition
float add = 37.2f + -2.6f; // result: 34.6
System.out.println(add);
// subtraction
float subtract = 45.1f - 10.3f; // result: 34.8
System.out.println(subtract);
// multiplication
float multiply = 26.3f * 1.7f; // result: 44.71
System.out.println(multiply);
// division
float division = 37.1f / 4.8f; // result: 7.729166
System.out.println(division);
// modulus
float modulus = 37.1f % 4.8f; // result: 3.4999971
System.out.println(modulus);6. double
A double is a double-precision 64-bit floating point number.
- Occupies
8bytes. - The default value is `0.0D`.
- It can store a min value of
-2^1074and a maximum value of2^1023.
double d1 = 0d;
double d2 = -0d;
System.out.println(d1 == d2); // true
System.out.println(1d / d1); // Infinity
System.out.println(1d / d2); // -Infinity
System.out.println(Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY / Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY); // NaNdouble A = -7162.37;
double B = 974.21;
double C = 658.7;
double addedDoubles = B + C; // 315.51
double subtractedDoubles = B - C; // 1632.91
double scientificNotationDouble = 1.2e-3; // 0.00127. char
A char can store a single 16-bit Unicode character. A character literal is enclosed in single quotes.
- Occupies
2bytes. - The default value is
0. - It can store a minimum value of
\u0000(0in the decimal representation, also called thenullcharacter) and the maximum of\uffffor(2^16 - 1). - The char values are
A,B,a,d, etc.
char myChar = 'u'; // 'u'
char myChar2 = '5'; // '5'
char myChar3 = 65; // 'A'8. boolean
A boolean can store one of two values, either true or false.
- Occupies
1bytes. - The default value is
false. - There is no min or max for
booleandata type.
boolean a = true; // true
boolean b = false; // false
boolean notA = !a; // false
boolean notB = !b; // true
boolean aAndB = a && b; // false
boolean aOrB = a || b; // true
boolean aXorB =a ^ b; // true