How to reverse the letters in a string in Java
In this article, we'll learn various ways to reverse strings in Java. An algorithmic approach with a flow chart and steps. Using java API methods to solve this problem and rotate kth elements or characters in an array.
Introduction
In Java, a string represents a sequence of characters like "Hello world." Strings are constants. Their values can't be changed once created.
In this Answer, we’ll use a method that takes an array of characters and reverses the letters. We’ll discuss how to reverse characters in a string without additional space. The question of how to reverse a string is one of the fundamental questions asked in the coding interviews.
Popular companies such as Facebook, Apple, Amazon, and Adobe ask this question in their interviews.
Why use an array of characters instead of a string?
We use an array to manipulate strings in a place. Since we’ll modify the input, we need a mutable type like an array rather than Java’s immutable strings.
Problem statement
Write a method that takes an array of characters and reverses the letters in place.
Example
Example 1
Input: ["a", "p", "p", "l", "e"]
Output: ["e", "l", "p", "p", "a"]Example 2
Input: ["O", "r", "a", "n", "g", "e", "s"]
Output: ["s", "e", "g", "n", "a", "r", "O"]Example 3
// Special characters
Input: ["$", "%", "#", "H", "e", "l", "l", "o", , "S", "p", "e", "c", "i", "a", "l", , "S", "t", "r","i", "n", "g", "#", "#"]
Output: ["#", "#", "g", "n", "i", "r", "t", "S", ,"l", "a", "i", "c", "e", "p", "S", , "o", "l", "l", "e", "H", "#", "%", "$"]Note: The algorithm needs to run in O(1) space. When we say that we’ll reverse characters without extra space, we mean that we shouldn’t create any extra memory. Also, an in-place algorithm refers to modifying the original input.Thought process
In general, an in-place algorithm will require swapping elements.
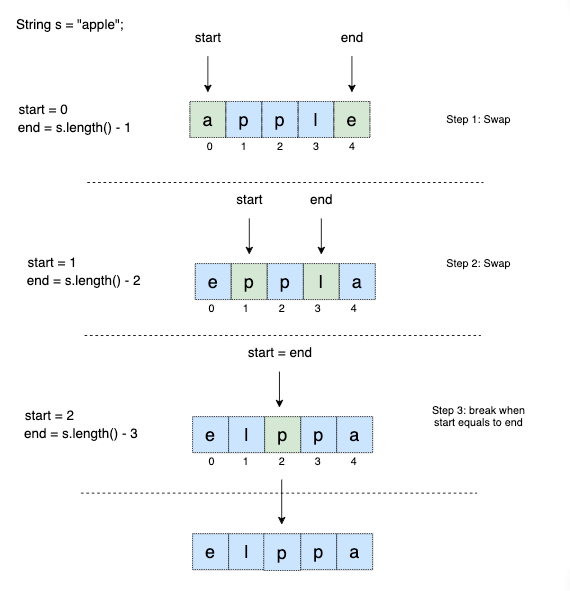
In this program, we swap the string's first and last characters. We repeat it until we reach the middle of the array. Let’s look at an illustration of this:
Flowchart
Solutions
In-place algorithm
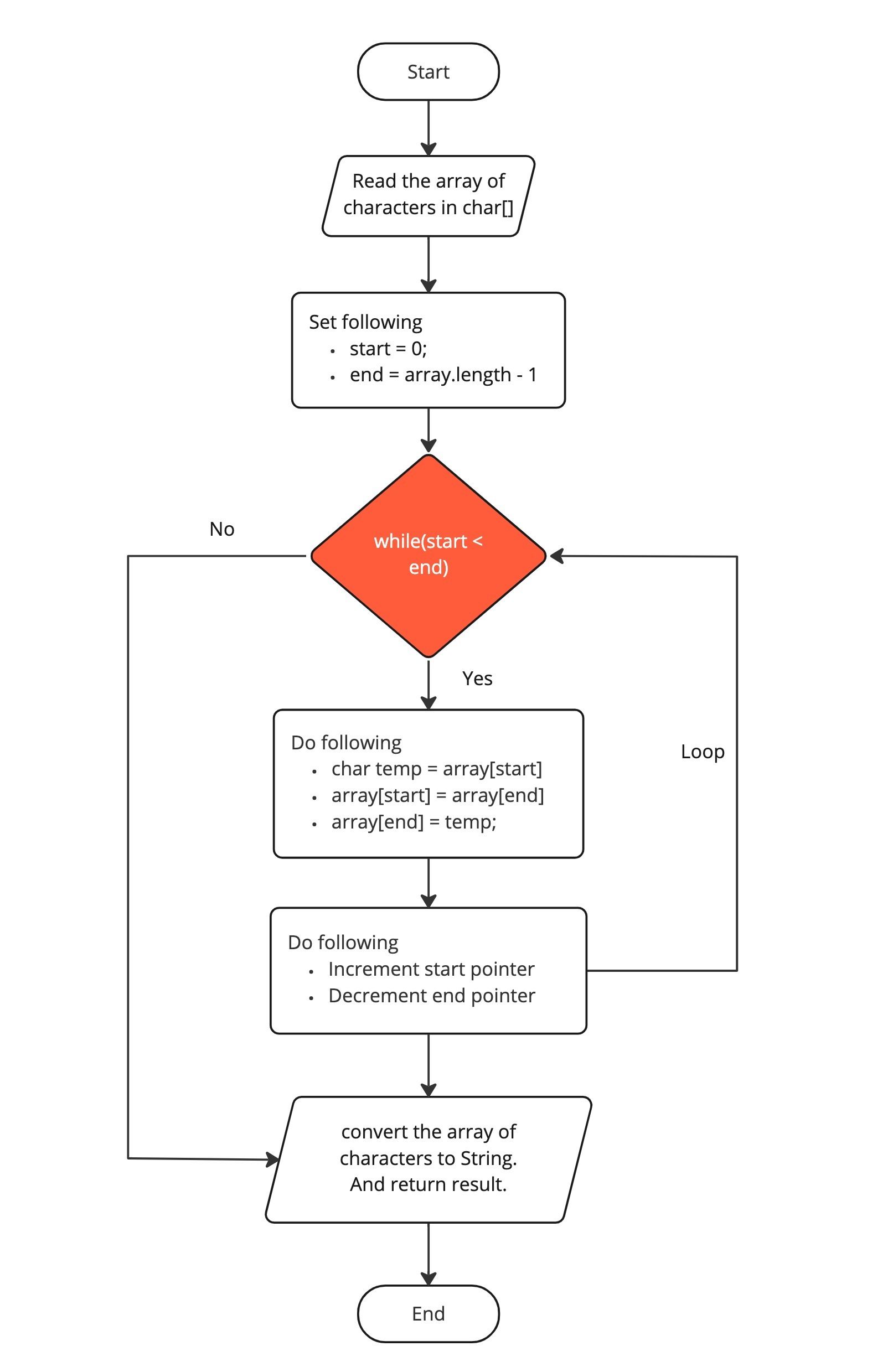
We’ll consider two variables start and end that start from 0 and s.length() - 1.
For each iteration, we'll do the following:
- Swap the characters and update the
startandendpointers. - Break the loop when
startandendpointers are equal.
Code
public class ReverseString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String first = "apple";
String second = "Oranges";
String specialInput = "$%#Hello Special String##";
System.out.println(reverseString(first.toCharArray()));
System.out.println(reverseString(second.toCharArray()));
System.out.println(reverseString(specialInput.toCharArray()));
}
public static String reverseString(char[] charArray) {
//base case
if (charArray == null) return "";
if (charArray.length == 1) return new String(charArray);
int start = 0;
int end = charArray.length - 1;
while (start < end) {
char ch = charArray[start];
charArray[start] = charArray[end];
charArray[end] = ch;
start++;
end--;
}
return new String(charArray);
}
}
Explanation
- For base cases, we’ll follow these steps to run our algorithm on the given input:
- Line 14: We’ll check if the given input is
null. If it’snullthen return an empty string"". - Line 15: We’ll check if the given array length equals
1. If it’s1then return the exact same input.
- Line 14: We’ll check if the given input is
- Lines 17 and 18: We’ll initialize two pointers
startandendrespectively, and point them to thestartandendindices of the array. - We’ll use the
whileloop to iterate over the array.- On each iteration, we swap the elements present on the indices
startandend. - We increment the
startandendpointers. - We run the loop until
startandendindices cross each other, and while loop breaks. - Line 28: We’ll return the resultant input.
- On each iteration, we swap the elements present on the indices
Complexity analysis
- Time Complexity: Use
O(N)to swapN/2elements, whereNis the length of the input string. - Space Complexity: Use
O(1); it's a constant space solution.
Java reverse()
We can re-use the existing java methods to reverse a string quickly, but it is wise to know how to solve a problem using algorithmic skills. This will help you drill down some of the more complex issues.
Let's see how Java reverses a string.
Code
public class ReverseString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String first = "apple";
String second = "Oranges";
System.out.println(reverseString(first));
System.out.println(reverseString(second));
}
static String reverseString(String s) {
return new StringBuilder(s).reverse().toString();
}
}
Explanation
- We used
StringBuilderto wrap the input, which converts the input string to an array of characters. - We’ll use the
.reverse()function to reverse the string builder array of elements. - We used the
toString()function to convert theStringBuilderinstanceStringAnd we return it.
Bonus
Let’s modify the algorithm to understand how we’ll use the character swaps and thought processes.
Example
Example 1
Input: ["a", "p", "p", "l", "e"], K = 2
Output: "paple"Example 2
Input: ["O", "r", "a", "n", "g", "e", "s"], K = 3
Output: "arOnges"Algorithm
We need to consider two variables start and end which starts from 0 and (k-1).
For each iteration, we’ll do the following:
- If
Kvalue is greater than the length of the array. Then we do a modulo operation to get the correct number of characters we need to reverse. This will be done by modulo operation -K = K % charArray.length. - Swap the characters and update the
startandendpointers. - Break the loop when
startandendpointers are equal.
Solution
public class ReverseKCharacters {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String first = "apple";
String second = "Oranges";
System.out.println(reverseString(first.toCharArray(), 7));
System.out.println(reverseString(second.toCharArray(), 3));
}
public static String reverseString(char[] charArray, int K) {
if (charArray == null) return "";
if (charArray.length == 1) return new String(charArray);
K = K % charArray.length;
int start = 0;
int end = K - 1;
while (start < end) {
char ch = charArray[start];
charArray[start] = charArray[end];
charArray[end] = ch;
start++;
end--;
}
return new String(charArray);
}
}
Explanation:
- For base cases, we’ll follow these steps to run our algorithm on the given input:
- Line 11: We’ll check if the given input is
null. If it’snullthen return an empty string"". - Line 15: We’ll check if the given array length equals
1. If it’s1then return the exact same input.
- Line 11: We’ll check if the given input is
- If
Kvalue is greater than the array length, we do amodulooperation to get the exact number of letters we need to reverse byK = K % charArray.length. - Lines 15 and 16: We’ll initialize two pointers
startandendrespectively, and point them to thestartandendindices of the array. - We’ll use the
whileloop to iterate over the array.- On each iteration, we swap the elements present on the indices
startandend. - We increment the
startandendpointers. - We run the loop until
startandendindices cross each other, and while loop breaks. - Line 26: We’ll return the resultant input.
- On each iteration, we swap the elements present on the indices
Complexity analysis
- Time Complexity:
O(K)to swapKelements, whereKis the number of characters we need to reverse. - Space Complexity:
O(1)is a constant space solution.
Conclusion
If you want to solve this problem using problem-solving skills, we have covered it here.
Like I say all the time, problem-solving is a mind-sport or e-sport. Don't expect super quick wins. It takes time to learn and master the skills to break down a problem into smaller pieces and solve them individually.
I hope this article helped you! Thank you for reading.