Two-Dimensional Arrays
What are 2D arrays?
Two-dimensional(2D) arrays can be defined as "arrays within an array" or "arrays of arrays." It is a grid-like structure where the rows and columns are indexed.
Theoretically, you can think of normal arrays as 1D or One-Dimensional arrays with a single row and multiple columns.
Like normal arrays, 2D arrays are static(fixed-size). In memory, items are organized sequentially, one after another.
The items could be Integer, String, Object, – anything. The items are stored in contiguous (adjacent to each other) memory locations.
Illustration
A simple sketch with N rows and M columns as follows. To access elements, you need to query using its corresponding row index and column index.
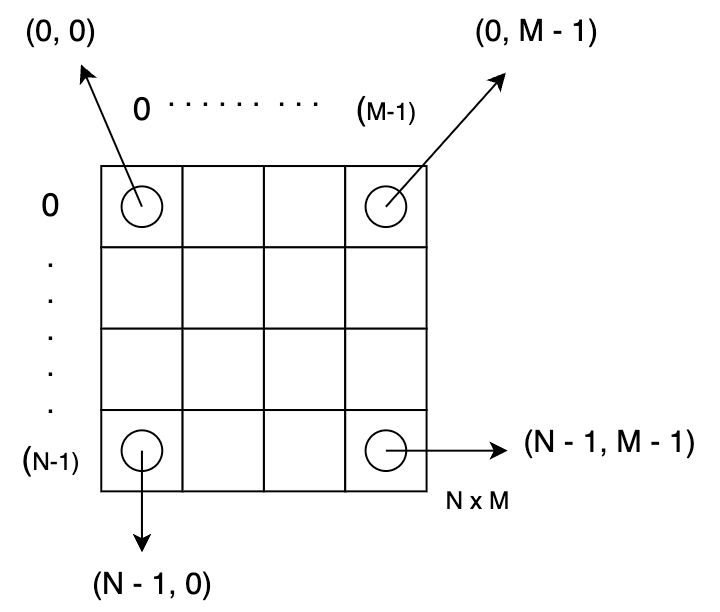
The following is another illustration with indexes inside the table for easy reference.
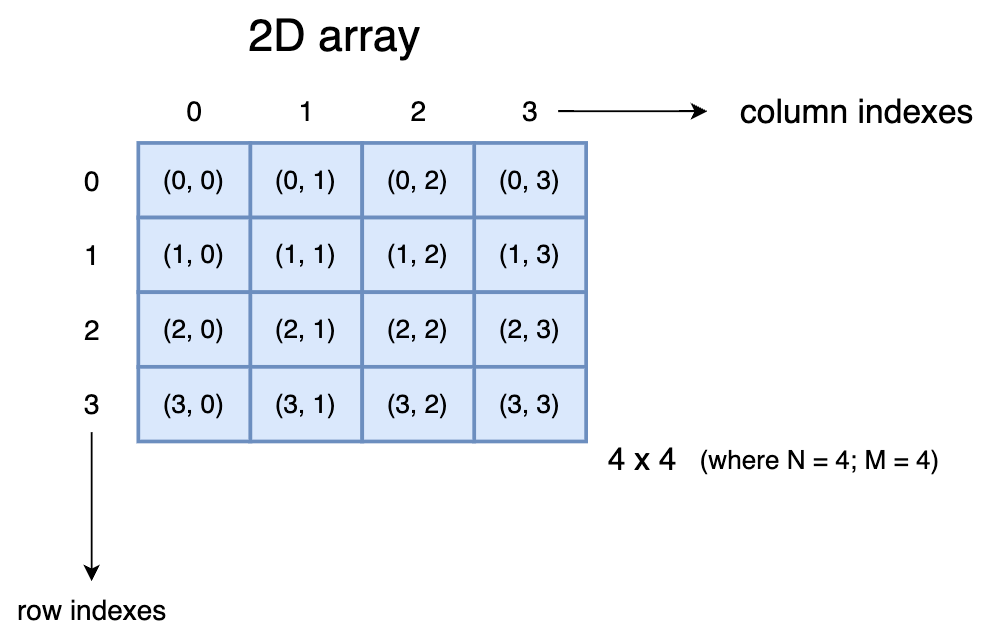
Declaration and initialization
To declare a 2D array, you need to specify the data type of the elements and the dimensions. The general declaration of a 2D array is:
dataType[][] arrayName = new dataType[rows][columns];
Here's an example of creating a 2D array of integers with 4 rows and 4 columns. To access the last element of the 2D array, we give A[3][3].
With this knowledge, if there are N rows and M columns, then the array hold NXM elements in it.
There are two ways we can declare and initialize 2D arrays.
// approach 1
int[][] grid = new int[3][3];
grid[0][0] = 1;
grid[0][1] = 2;
grid[0][2] = 3;
grid[1][0] = 4;
grid[1][1] = 5;
grid[1][2] = 6;
grid[2][0] = 7;
grid[2][1] = 8;
grid[2][2] = 9;
// approach 2
int[][] grid = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6},
{7, 8, 9}
};
This creates a 2D array named grid with 3 rows and 3 columns. The indexes of the elements in the array range from 0 to (rows-1) for the rows and 0 to (columns-1) for the columns.
2D arrays in Java are useful for representing grids, matrices, and tables where data needs to be organized in rows and columns.
Next, a small illustration helps you understand how we access array elements using their indexes.
How do you access elements?
Following is a simple sketch of a 2D array A with a capacity of N rows and M columns.
int[][] A;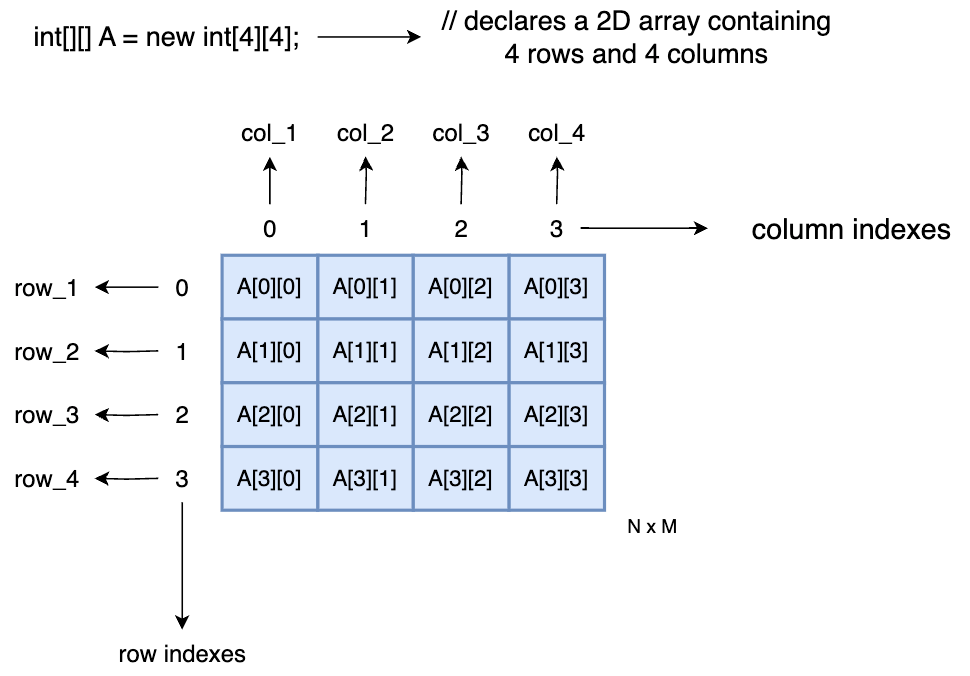
If you want to access the first element, you need to give A[0][0], which is A[rowIndex][colIndex].
What happens if we do A[4][4], A[4][3], and A[3][4]? 🤔
You guessed it. We run into ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 4 out of bounds for length 3
at dev.ggorantala.ds.arrays.twodimensional.TwoDimensionalArray.main(TwoDimensionalArray.java:27)You can access and modify individual elements in a 2D array using the row and column indexes.
For example, to access the element at row 1 and column 2 of the "grid" array, you would use:
int element = A[1][2];Similarly, you can assign a value to an element in the array:
A[1][2] = 42;At most, we can access the last element of the array using A[N-1][M-1].